Kidney stones – Symptoms, causes, types, and treatment
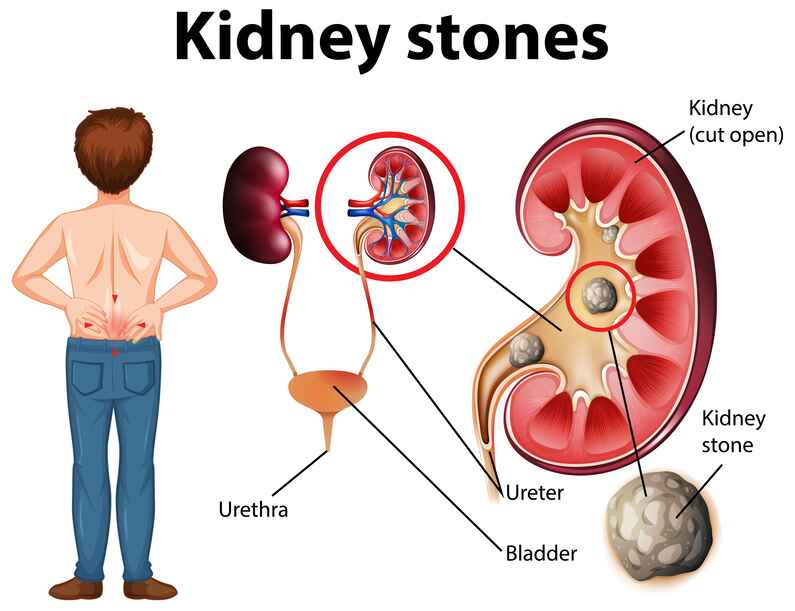
Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever felt a sharp pain in your back or side and wondered what it could be? If you’ve heard tales of kidney stones, you might have been on the right track. Kidney stones are a common affliction that many people face, but luckily, they are manageable and preventable with the right information and lifestyle choices. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of kidney stones, exploring their symptoms, causes, types, and treatments. Let’s embark on this journey together!
What Are Kidney Stones?
Definition and Overview
Kidney stones, scientifically known as renal calculi, are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. They can be as tiny as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Sounds painful, doesn’t it? These stones can affect any part of your urinary tract, from the kidneys to the bladder.
How Do Kidney Stones Form?
Crystallization Process
Kidney stones form when your urine contains more crystal-forming substances such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid than your urine can dilute. At the same time, your urine might be deficient in substances that prevent crystals from sticking together.
Factors Contributing to Stone Formation
Factors like dehydration, high salt intake, and certain medical conditions can influence stone formation. Imagine your kidneys working like a coffee filter. When there’s too much debris (crystal-forming substances) and not enough liquid to wash it through, clogs (stones) form.
Types of Kidney Stones
Calcium Stones
The most common variety, calcium stones, often come as calcium oxalate, and they form due to high oxalate levels combined with calcium in the urine.
Uric Acid Stones
These stones develop when uric acid levels in the urine are too high, often linked to a protein-rich diet. They’re more common in men than women.
Struvite Stones
Often stemming from urinary tract infections, struvite stones can grow quickly and become quite large. They’re more prevalent in women due to higher infection rates.
Cystine Stones
A rare type, cystine stones occur when the kidneys excrete too much of certain amino acids. It’s typically a genetic disorder.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Pain and Discomfort
One of the hallmark symptoms is intense pain in the back, side, or groin. This pain can come and go, and it often arrives in waves.
Urinary Symptoms
You might notice a burning sensation while urinating, frequent urges to urinate, or even spotting blood in your urine.
Additional Symptoms
Fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting can also accompany kidney stones, especially if an infection is present.
Causes of Kidney Stones
Dietary Factors
High intake of salt, sugar, and protein can contribute to stone formation. Think twice before indulging in that third helping of salty fries!
Medical Conditions
Conditions like hyperparathyroidism, urinary tract infections, and kidney diseases can increase your risk.
Genetic Predisposition
If kidney stones run in your family, you might be genetically predisposed to developing them.
Dehydration
Insufficient fluid intake results in less urine production, making it easier for stones to form.
Risk Factors for Kidney Stones
Age and Gender
Individuals aged 30-50 are more likely to develop stones. Men are more prone to kidney stones than women.
Lifestyle Factors
Obesity, lack of exercise, and a sedentary lifestyle can also increase your risk.
Geographical Influence
People living in warmer climates might be more susceptible due to higher dehydration rates.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Medical History Review
Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms to get a clear picture.
Imaging Techniques
CT scans, X-rays, and ultrasounds are commonly used to detect stones and assess their size and location.
Laboratory Tests
Urinalysis and blood tests help identify the substances contributing to stone formation.
Treatment Options for Kidney Stones
Medications
Pain relievers, alpha-blockers, and medications to prevent stone formation are often prescribed.
Lifestyle Changes
Increasing fluid intake, dietary modifications, and regular exercise can prevent recurrence.
Surgical Procedures
For larger stones, options like shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, and percutaneous nephrolithotomy are available.
Preventing Kidney Stones
Hydration Importance
Drinking plenty of water is the simplest way to prevent kidney stones. Aim for at least eight glasses a day.
Dietary Modifications
Reducing salt, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods can make a significant difference.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular visits to your healthcare provider help catch potential issues early.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Hydration Tips
Consistently drinking water and consuming hydrating foods like watermelon can help.
Dietary Recommendations
Maintaining a balanced diet, low in salt and high in fruits and vegetables, is beneficial.
Herbal Remedies
Some believe that herbal remedies like dandelion root and nettle leaf can support kidney health.
Complications Associated with Kidney Stones
Infection Risks
If stones obstruct the urinary tract, they can cause severe infections, potentially leading to sepsis.
Kidney Damage
Persistent obstruction can damage your kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease.
Recurring Stones
Once you develop kidney stones, you’re more likely to develop them again.
Living with Kidney Stones
Managing Pain
Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage minor discomfort.
Avoiding Triggers
Knowing what triggers your stones, whether it’s certain foods or dehydration, can help you avoid recurrence.
Support Systems
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice.
When to See a Doctor
Emergency Symptoms
If you experience severe pain, blood in your urine, or fever, seek medical attention immediately.
Recurring Symptoms
Frequent or recurring symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Kidney stones might seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and proactive measures, you can manage and prevent them effectively. By staying hydrated, making smart dietary choices, and seeking timely medical advice, you can keep kidney stones at bay. Remember, your health is in your hands—literally!
FAQs
What are the early signs of kidney stones?
Early signs include sharp pains in the side or back, pain during urination, and frequent urination.
Can diet alone prevent kidney stones?
While diet plays a crucial role, hydration and genetics also significantly impact stone formation.
Are kidney stones more common in men or women?
Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women.
How long does it take to pass a kidney stone?
It can take a few days to several weeks to pass a kidney stone, depending on its size and location.
Is kidney stone surgery risky?
Like any surgery, there are risks, but modern techniques have made it safer and more effective. Always consult your doctor for personalized advice.