What Exactly is Diverticulitis? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
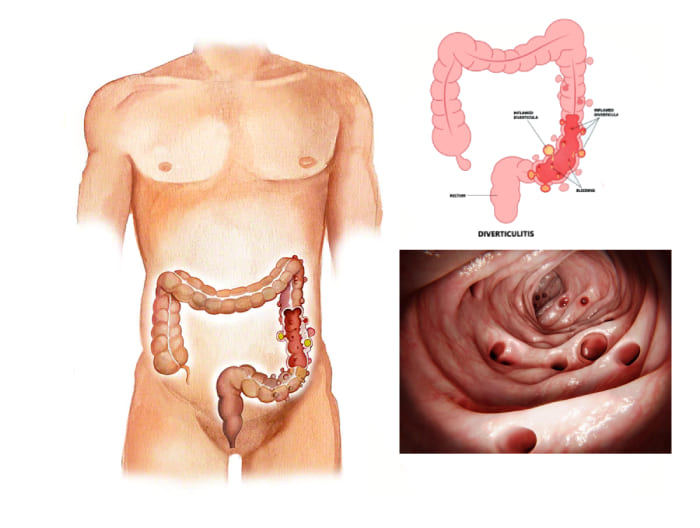
Diverticulitis is a condition that can significantly affect your quality of life. It involves the inflammation or infection of bulges (diverticula) in your digestive tract. While the condition itself may sound complex, breaking it down into its core components – causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures – can offer clarity and aid in managing or even preventing its onset.
Symptoms
The symptoms of diverticulitis can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. It’s crucial to be aware of these signals, as they often serve as the primary alert that prompts an individual to seek medical attention. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent pain, typically in the lower left side of the abdomen
- Fever and chills
- Bloating and gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- A change in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea)
It’s the discomfort and often the pain that brings most people to the doctor’s office, acknowledging that something isn’t quite right within their bodies.
Causes
Diverticulitis stems from the formation of diverticula, which are small bulges or sacks that can form in the lining of the digestive system. These pockets are particularly prevalent in the colon. When one or more of these diverticula become inflamed or infected, diverticulitis occurs. While the precise cause of diverticula formation isn’t entirely understood, it’s believed to be related to a low-fiber diet, which can lead to increased colon pressure and subsequently, to these pockets forming.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing diverticulitis, including:
- Age (it’s more common in people over the age of 40)
- Being overweight or obese
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- A diet high in animal fats and low in fiber
- Certain medications, including steroids and opiates
Understanding these risk factors is essential in taking steps toward prevention.
Prevention
One of the most effective ways to prevent diverticulitis is by adopting a healthier lifestyle. This includes:
- Eating a high-fiber diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
- Getting regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
Incorporating these habits not only reduces the risk of developing diverticulitis but also contributes to overall well-being.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms of diverticulitis, especially if you have unexplained or persistent abdominal pain, fever, or changes in bowel habits. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Treatment
Treatment for diverticulitis depends on the severity of your symptoms. Mild cases can often be managed at home with rest, diet modifications, and antibiotics. More severe cases may require hospitalization, intravenous antibiotics, or even surgery in cases where there is a complication like a perforation, abscess, or blockage.
- Antibiotics to treat infection
- Pain relievers
- A liquid diet to allow the colon to heal
- Surgery, in severe cases
Embracing a lifestyle that supports the health of your digestive system can not only alleviate symptoms but, in some scenarios, may prevent them from arising in the first place.
In conclusion, while diverticulitis can present significant challenges, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers you to take control of your health. By being proactive about preventive measures and knowing when to seek medical intervention, you can manage or even prevent diverticulitis, leading to a healthier and more comfortable life. Remember, taking care of your digestive health is not just about preventing a particular condition but about fostering overall well-being.